Companies are dealing with a nonstop flow of data from apps, devices, and users. The hard part isn’t getting the data. It’s acting on it fast enough to make a difference. That’s where data streaming comes in. Instead of waiting for data to be collected and processed later, streaming lets you work with it as it moves. Financial services can spot fraud in real time. Retailers can adjust inventory on the fly. Security teams can respond to threats as they happen. Streaming makes real-time decisions possible across every industry.
What is data streaming?
Data streaming is a method of continuously transmitting and receiving data in real-time, enabling analysis and processing of the data as it flows. Unlike traditional batch processing, where data is collected, stored, and processed in chunks, data streaming handles information incrementally. This allows companies to act on insights as they emerge. The approach is particularly crucial in today’s fast-paced, data-intensive world, where timely decision-making can provide a significant competitive advantage.
How does data streaming work?
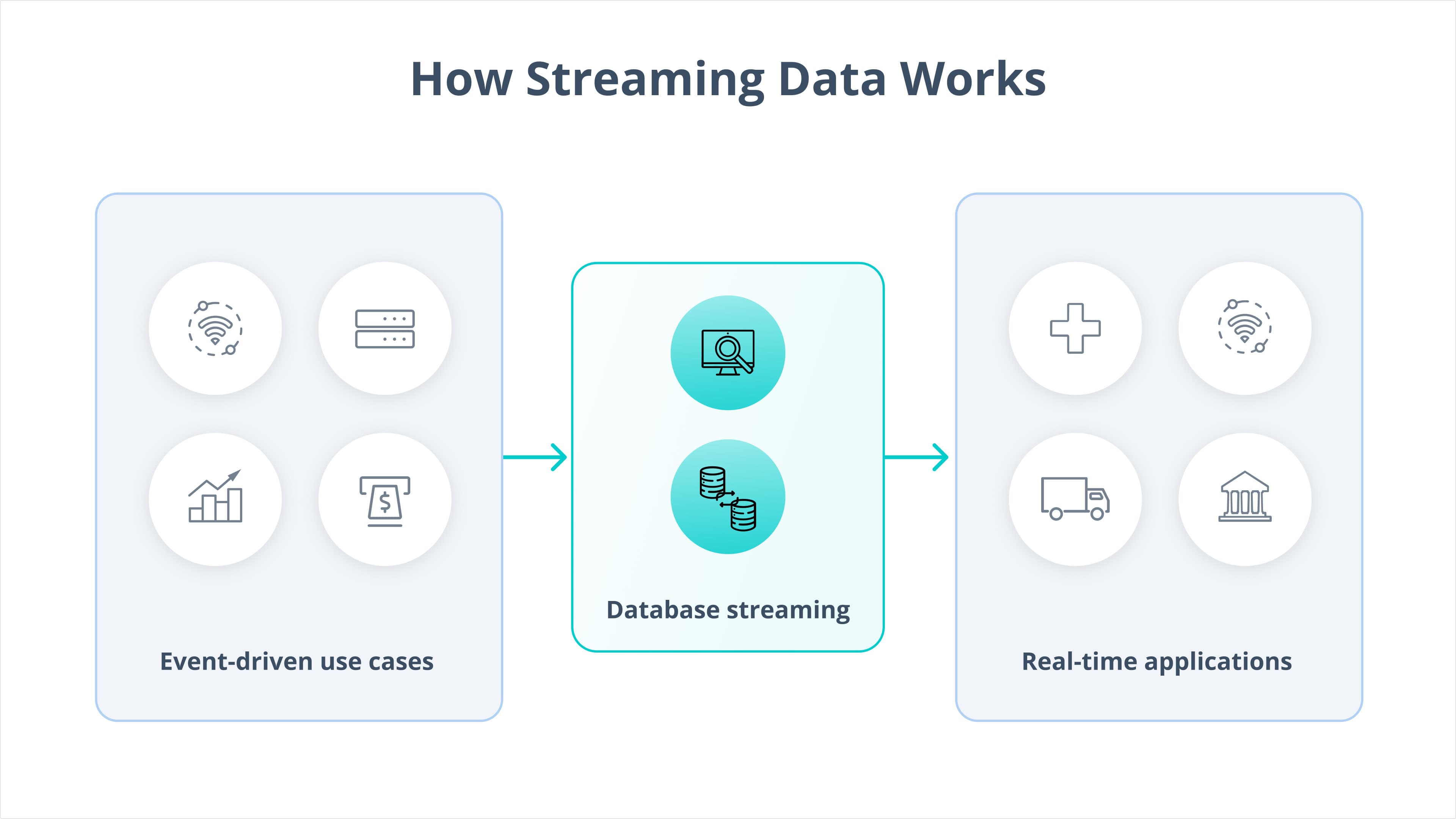
Data Sources: Where Does Streaming Data Come From?
Streaming data comes from the constant telemetry generated by apps, infrastructure (networks, servers, storage), and services. This includes system logs, metrics, traces, API calls, user interactions, and network activity. It’s the behind-the-scenes signal that powers everything from performance monitoring to threat detection.
Different industries rely on this telemetry in different ways. In financial services, real-time transaction data helps flag fraud the moment it happens. In manufacturing, telemetry from a wide range of devices can provide insight into usage and performance. In e-commerce, telemetry from web servers and APIs can detect slowdowns during checkout or sudden spikes in traffic that might impact conversion rates. In IT and security, streaming logs and metrics from endpoints and services help teams identify outages or active threats before they cause real damage.
Data Ingestion: How Is Streaming Data Collected?
The moment telemetry is generated, it needs to move quickly and efficiently. Cribl helps teams take control at this stage. It can route telemetry to the right tools, reshape formats, and reduce noise by dropping unneeded fields or entire events. Instead of sending everything to every destination, Cribl makes it possible to send only what’s relevant.
Real-Time Processing & Transformation
With streaming, data is processed as it flows. There’s no waiting for logs to land in storage or for daily jobs to run. This real-time pipeline allows teams to act fast.
A payment processor can flag suspicious activity mid-transaction. An SRE team can spot a CPU spike and start remediation before customers are affected. In e-commerce, a sudden increase in latency during checkout can trigger alerts and auto-scaling before revenue takes a hit. With Cribl in the pipeline, teams can enrich, redact, or transform data in motion to get the right context into the right system without delay.
Storage & Analytics
Some data needs to stick around. Some doesn’t. Streaming gives teams the flexibility to act now and store only what matters later. Real-time alerts can be triggered immediately while structured telemetry can be archived in a data lake or observability platform for longer-term analysis.
The takeaway is simple: telemetry doesn’t need to sit idle before it becomes useful. With the right tools, streaming data can drive real-time decisions across any environment.
What are the pros and cons of data streaming?
When assessing the merits of data streaming, it’s important to explore its specific pros and cons. Let’s break them down real quick.
Pros:
Real-time business insights – Data streaming is crucial for businesses needing real-time information for informed decisions and quick responses to market changes.
Handling multiple data flows – It’s useful for processing data from multiple pipelines to cater to various user requirements.
System visibility – It helps IT organizations identify issues promptly, preventing them from escalating.
Scalability – Data streaming enables businesses to handle large and complex data sets, supporting rapid growth and demand.
Cons:
Data overload – Processing vast amounts of data in real-time can make it challenging to identify relevant information, potentially overwhelming businesses.
Cost – Implementing data streaming can be expensive. Especially if it necessitates new hardware and software investments.
Data loss or corruption – In real-time processing, there is a risk of data being lost or corrupted, with no opportunity for recovery.
Overhead – Data streaming requires extra storage and processing, adding to overhead. It’s crucial to assess its return on investment.
Data Streaming Use Cases
Data is a powerful approach that helps organizations make faster, smarter decisions by processing data the moment it’s created. Whether it’s detecting fraud in real time, powering IoT devices, or delivering personalized customer experiences, streaming data plays a key role in keeping modern systems responsive and efficient.
Let’s look at some of the most common and high-impact use cases—and how Cribl supports them behind the scenes.
Cybersecurity & Fraud Detection
Example: Banks and financial institutions use data streaming to detect fraud in real time—by analyzing transaction patterns and instantly flagging suspicious activity.
How Cribl Helps: Cribl Stream enhances threat detection by optimizing, filtering, and routing security logs in real time, ensuring faster response and reduced alert fatigue for security teams.
IoT and Smart Devices
Example: Smart home devices like thermostats, lights, and security cameras rely on continuous data streams to make real-time decisions, adjusting settings, sending alerts, or activating functions instantly.
In industrial settings, streaming telemetry data helps monitor equipment usage, performance, and anomalies, enabling predictive maintenance and reduced downtime.
How Cribl Helps: Cribl efficiently handles high-volume telemetry data, allowing businesses to filter, enrich, and route relevant information to the right destinations without overwhelming their systems.
Customer Experience & Personalization
Example: E-commerce platforms and digital services use real-time data to personalize customer experiences, such as recommending products based on live browsing behavior or tailoring content based on user interactions.
How Cribl Helps: Cribl Stream enables seamless log and event stream routing, empowering businesses to harness behavioral data for analytics and personalization efforts while controlling data volume and cost.
IT & System Monitoring
Example: IT operations teams rely on data streaming to monitor infrastructure health in real time, identifying performance issues or anomalies before they escalate into outages.
How Cribl Helps: By streamlining log data pipelines, Cribl enables teams to detect, enrich, and route critical signals in real time—improving observability and accelerating incident response.