New in Cribl 4.5, the Model Driven Telemetry Source enables you to collect, transform, and route Model Driven Telemetry (MDT) data.
In this blog, you’ll learn how to explore the YANG Suite to understand the wide variety of datasets available to transmit as well as how to configure the tools to get data flowing from Cisco IOS XE network devices to Cribl Stream.
As Cisco recommends, you’ll use the YANG data modeling language along with Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) to make the network devices dance, so to speak.
After a whirlwind tour of MDT history, we’ll explain all the pieces and get them running in no time. So, let’s put on our Daft Punk helmets and see how network monitoring gets better, faster, and stronger with Cribl.

Why MDT?
(This section explains why network engineering and security operations teams are moving away from SNMP to MDT. If you prefer to dive right into our configuration tutorial, skip ahead to YANG Suite and NETCONF: Making Cisco devices dance.)
The network monitoring space is evolving. SNMP trap and polling solutions have been around since the 1980s, and over the years (and v2 & v3 versions), these solutions have worked well, providing network engineering and security operations teams with the level of transparency, granularity, and response latency that met the standards of the times. But yesterday’s network monitoring solutions are up against today’s growing demands. In today’s context, SNMP solutions are heavy. Polling solutions are pull-based, loading queues on network devices, impacting performance, and weighing down teams with non-scalable maintenance operations. Modern network teams demand modern solutions. They require finer-grained telemetry, real-time responses, and heightened scalability requirements that are not being met by legacy solutions.
As a direct response to these growing demands, network engineering and security operations teams are shopping and adopting Model Driven Telemetry (MDT) because it does so much more than SNMP. In contrast to SNMP solutions, MDT enables real-time streaming of telemetry data from network devices using a push-based, highly granular, and optimized model. These benefits are robust, and industry leaders are aware. If you’re already leveraging network devices from Cisco, Arista, Juniper, and Huawei, you’re probably aware that they’ve released support of MDT.
In the February 4.5 release, Cribl Stream introduces a new Model Driven Telemetry Source, allowing customers to collect, transform, and route MDT data as they wish. Let’s get into the details.
YANG Suite and NETCONF: Making Cisco Devices Dance
Cisco’s preferred approach for working with MDT is to use the YANG Suite of tools to configure network devices according to NETCONF. How do these elements interact?
YANG Models are data models that define what to collect from a device.
YANG Suite lets you explore and configure network devices, data models, and network protocols.
NETCONF is a protocol for transmitting data between YANG Suite and network devices.
This tutorial assumes that you’ve completed the following steps:
Install YANG Suite
Add a YANG Repository and YANG Module Set
Add a device to YANG Suite
Configure a device with NETCONF
Create a subscription XPath
If you’re unfamiliar with MDT and the YANG Suite, see Cisco’s in-depth tech guide and then follow up with the Cisco DevNet sandboxes where you can spin up virtual networks to tap into virtual Cisco devices. Here’s a tip: running the IOS XE on Cat8kv sandbox is the easiest way to obtain the YANG, NETCONF, and other prerequisites you’ll need for this tutorial. (We used this sandbox for testing when we wrote this blog post, too.)
(Optional) Exploring datasets in the YANG Suite
Log into YANG Suite.
Use the Analytics option to explore the catalog of data sets (YANG Modules) available from your Cisco device.
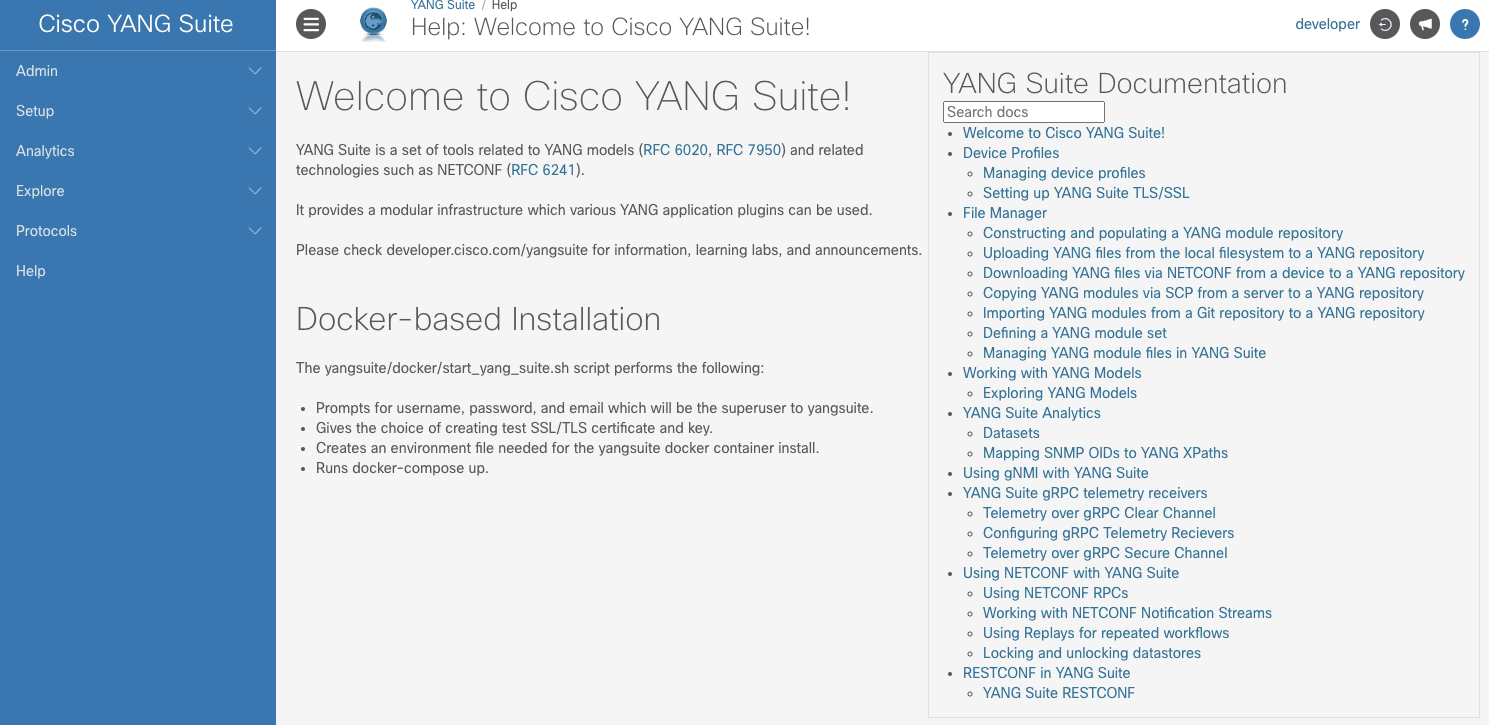
From the Cisco YANG Suite menu at left, select Analytics > Datasets and diffs.
From the Current YANG set drop-down, select the YANG set that you set up previously (in this example, the set is cat8000v-default-yangset).
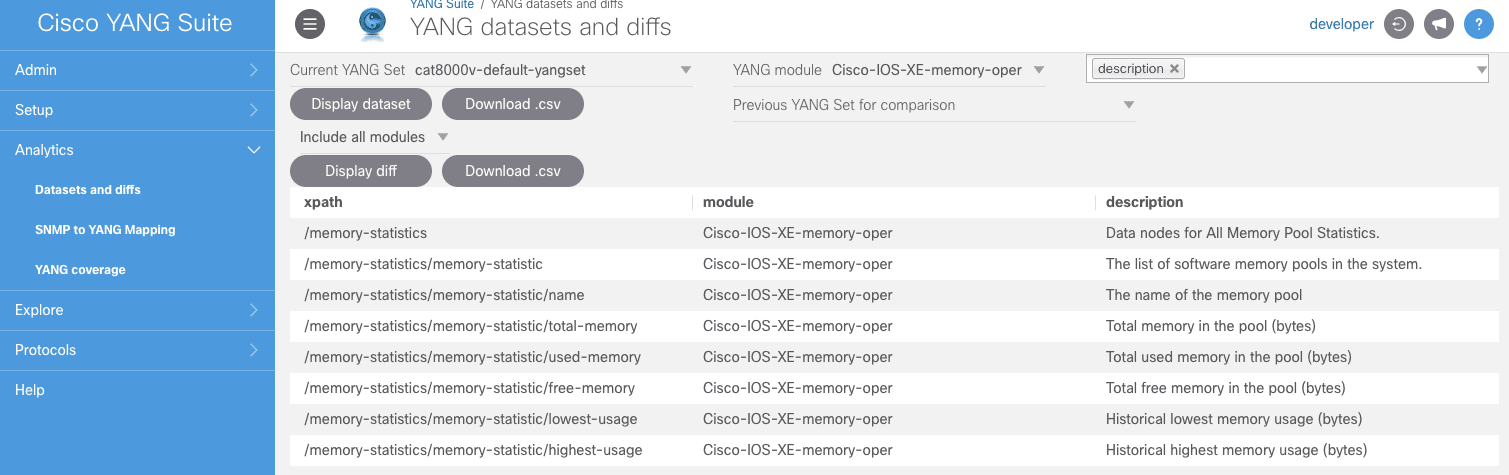
In the YANG Module drop-down, select a module. (In this example, we select Cisco-IOS-XE-memory-oper.)
In the Additional fields to include in dataset drop-down, select Description. This option is a good starting point for exploring and gaining more insight on what is available in the dataset.
Click Display dataset to see the XPaths associated with the elements and metrics your dataset supports. (Why XPaths? Because NETCONF is an XML-based protocol.)
Using YANG Suite to send your device’s data to Cribl
Let’s configure NETCONF and a Device Subscription.
From the Cisco YANG Suite menu at left, select Protocols > NETCONF.
Select a YANG set and module. In this example, we’ll choose:
YANG set:
cat8000v-default-yangsetModule:
Cisco-IOS-XE-mdt-cfgClick Load Module(s).
When the module has loaded, its name will appear under Nodes in the window at left.
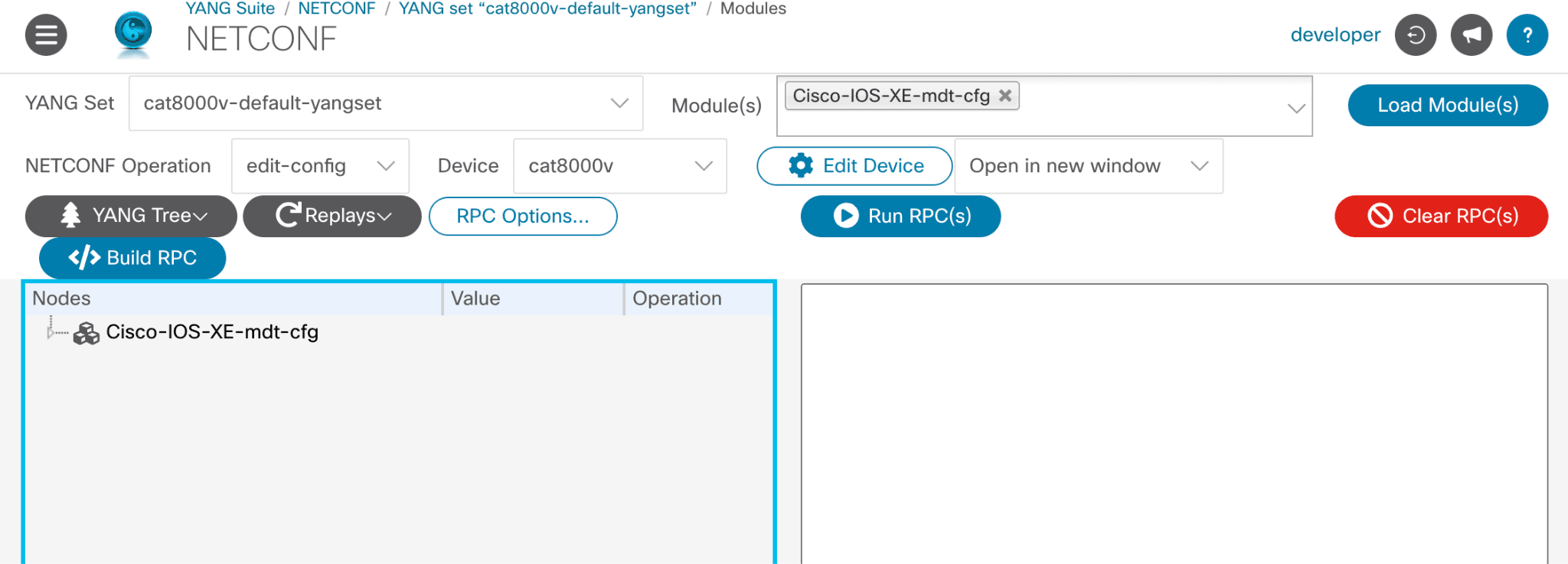
Use the drop-downs to set NETCONF Operation to edit-config and select the Device to configure (in this example, cat8000v).
Double-click on any branch in the module to expand its attributes as in the screenshot below. Of the values used in this example, two are required:
stream:
yang-pushencoding:
encode-kvgpb
Another, the XPath, needs to be one of the XPaths that your chosen dataset makes available. In this example, we chose an XPath for memory-related metrics:
XPath:
/memory-ios-xe-oper:memory-statistics/memory-statistic
Finally, there are attributes whose value is completely up to you. In this example, they are:
subscription-id: 100period: 1000
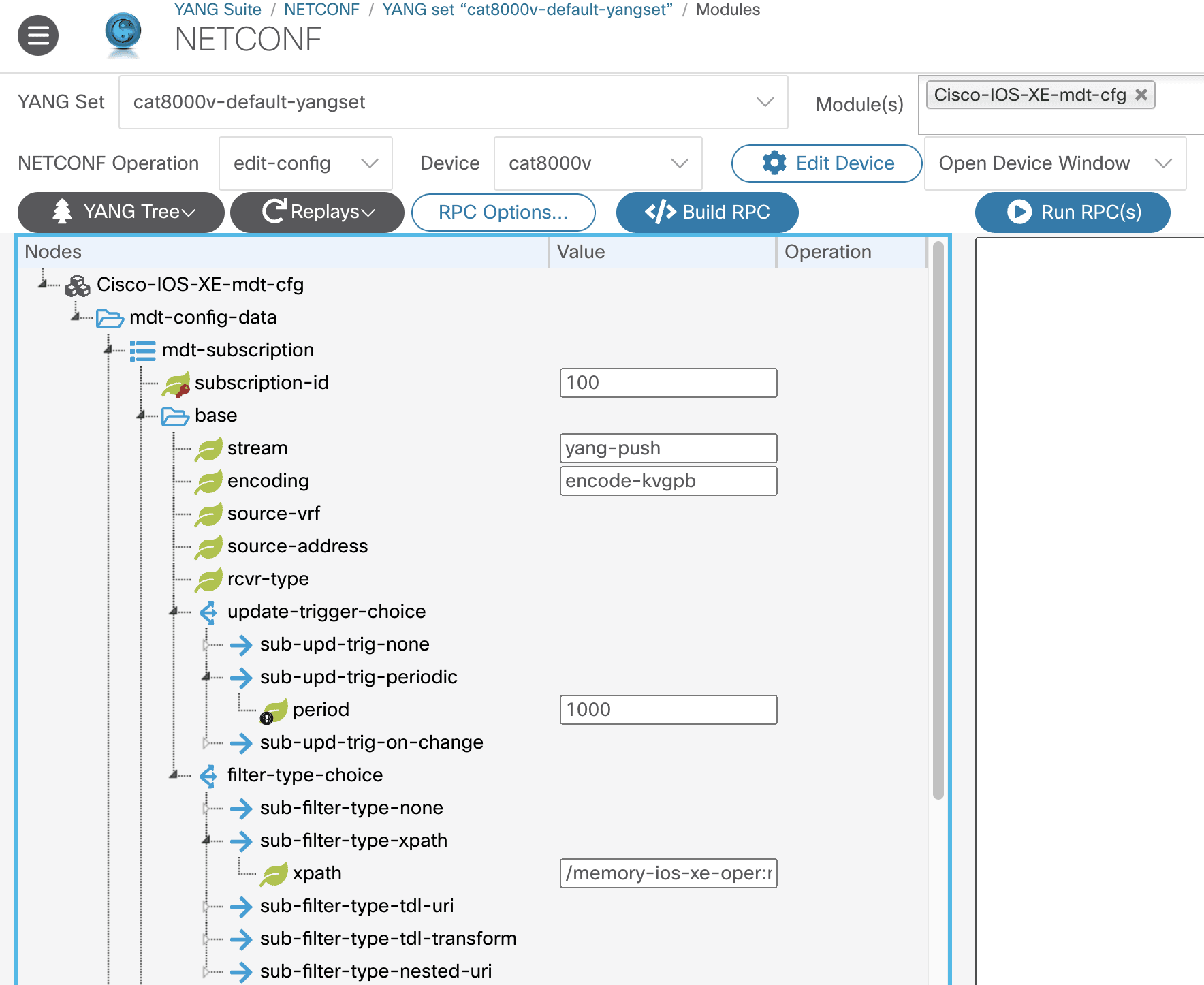
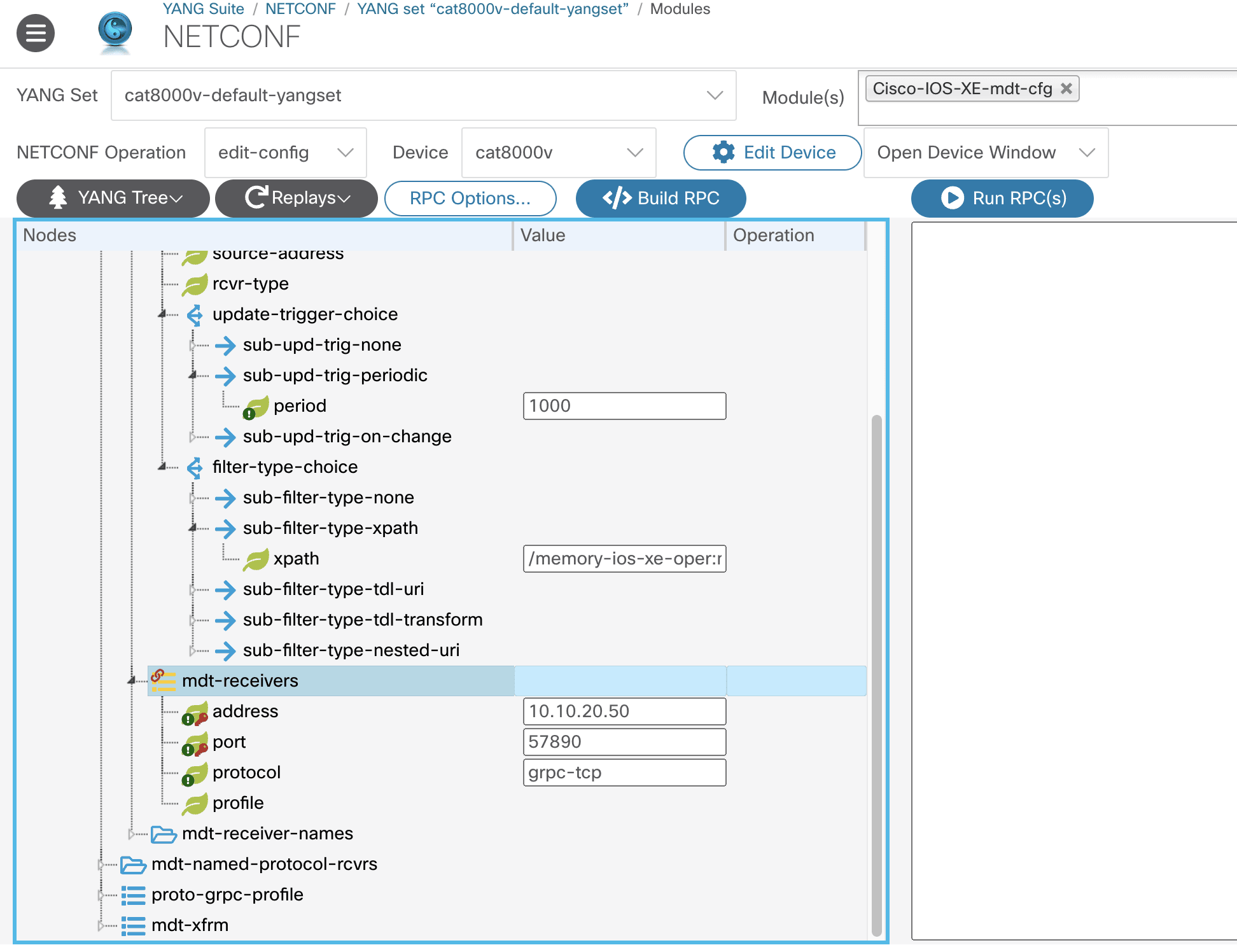
Further down the tree, locate and expand the mdt-receivers branch.
Enter the following values:
address: Enter the IP of your Cribl Stream instance.
port: Enter the port you plan to configure for your Cribl Model Driven Telemetry Source.
Note: MDT does not define a specific port. The port typically seen in MDT docs is 57000.
protocol:
grpc-tcpNote: For sending data to Cribl,
grpc-tcpis the only allowed value for the protocol attribute.
Now that you’ve chosen your desired Device Subscription values, YANG Suite will use them to build an RPC, also known as a code bundle.
Click Build RPC.
For simplicity, we’re walking through a use case where one XPath is sufficient to produce the elements and metrics we want to send to Cribl. In production, you might want to use multiple XPaths.
For each additional XPath, you’ll need to run Build RPC again in the following way:
Once the first RPC build has been completed, overwrite the XPath with the next one.
Click Build RPC again.
Repeat the first two steps as needed.
This procedure will append the content associated with each XPath to the RPC.
When you’ve built an RPC with all desired XPaths:
Use the drop-down above Run RPC(s) to choose how you want results displayed once the RPC has run.
Click Run RPC(s).
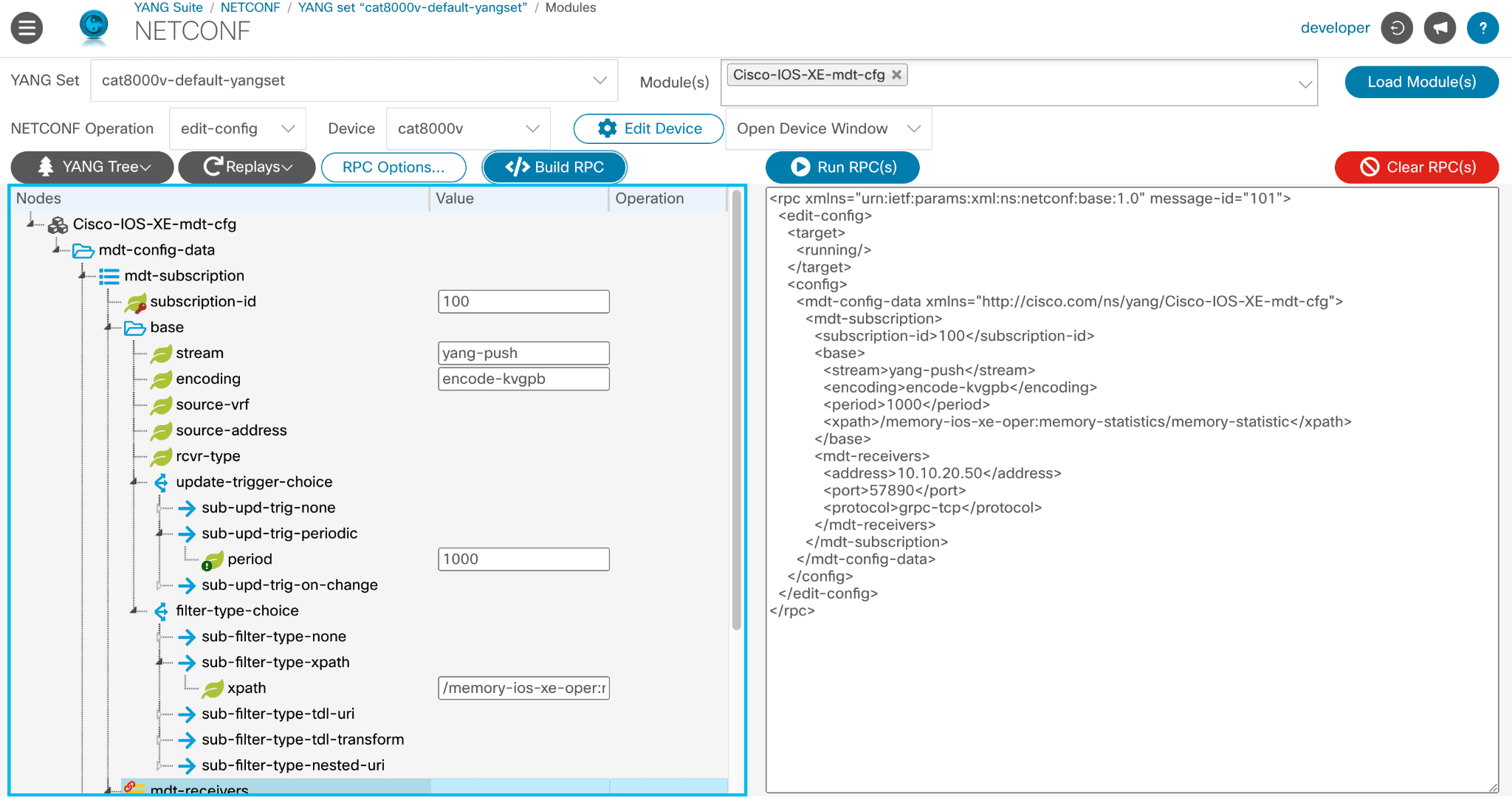
You will see a list of transmissions, including the RPC payload (also called an XML code bundle) and the NETCONF edit-config COMPLETE message.
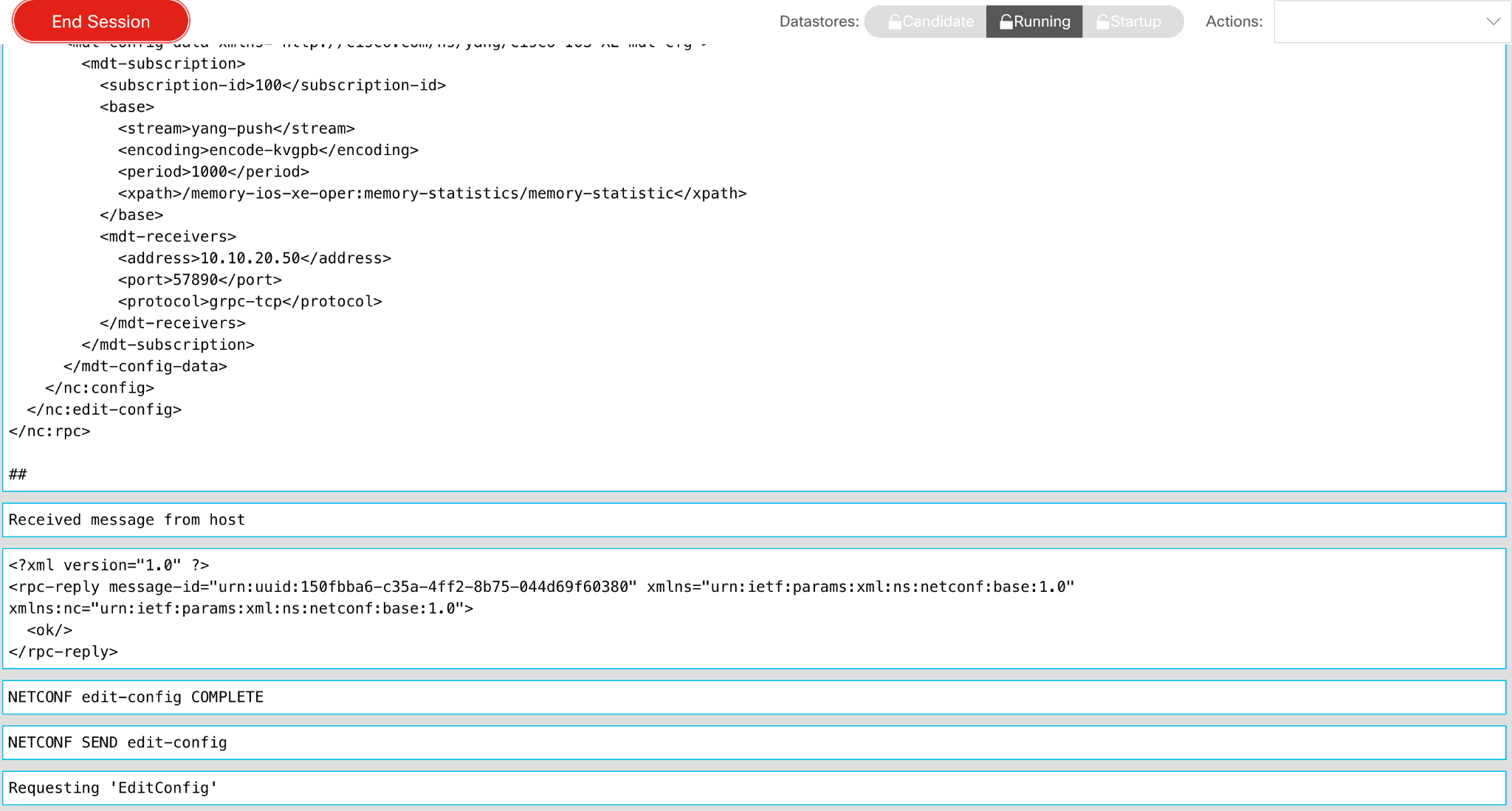
Configuring the Model Driven Telemetry Source in Cribl Stream
In Cribl Stream, add a new Model Driven Telemetry Source.
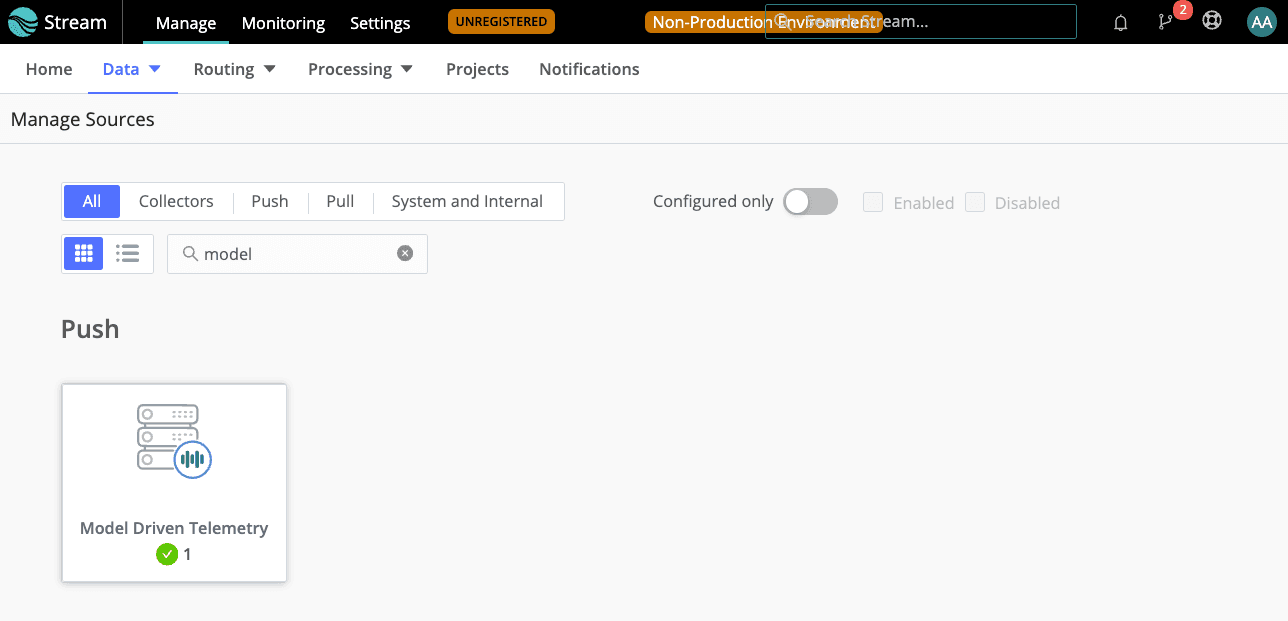
In the New Source modal:
Enter an Input ID.
Enter the Address.
Enter the same port you configured in NETCONF.
Click Save.
Commit and Deploy.
When Cribl Stream has finished deploying your changes:
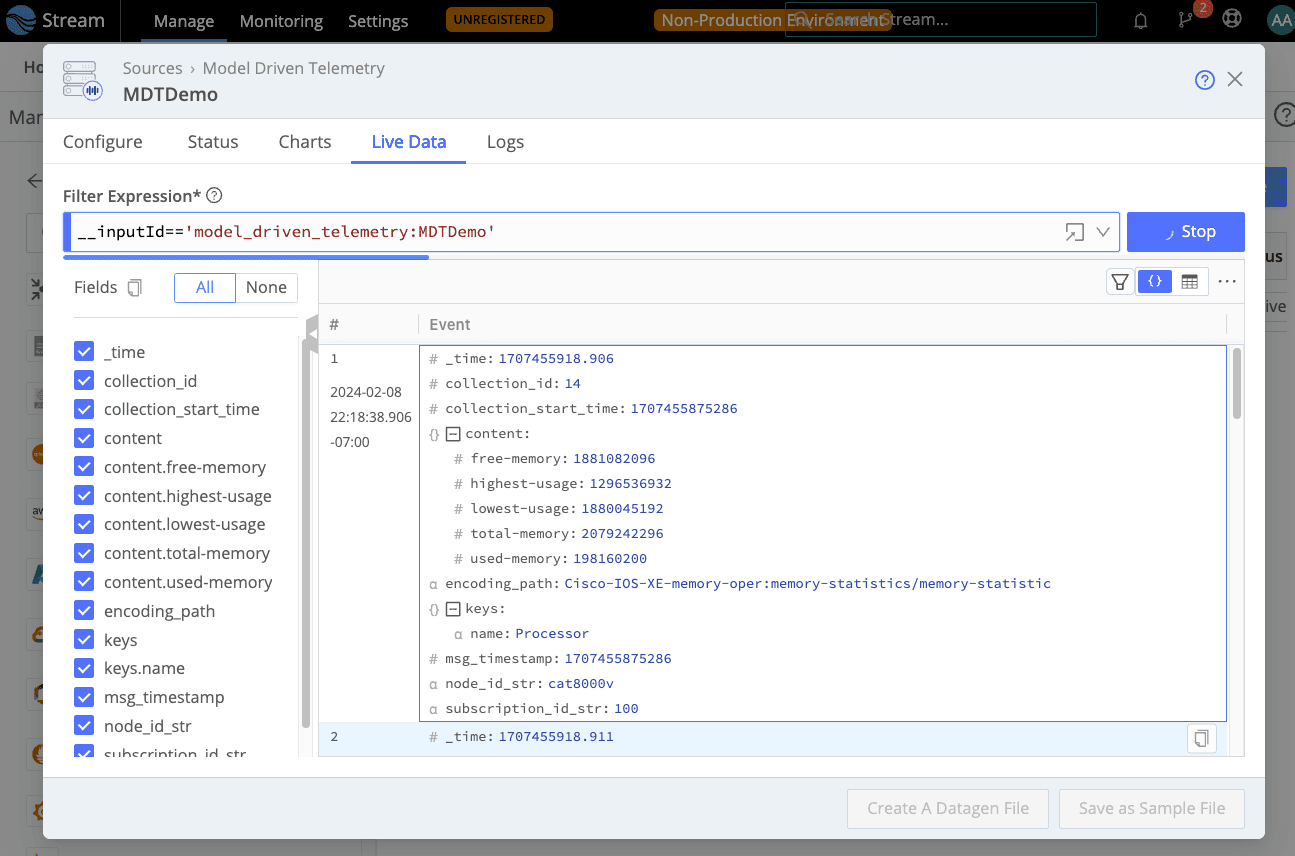
Navigate to the Live Data tab.
You’ll see events from your MDT device begin to roll in. Welcome to streaming network telemetry in Cribl Stream!
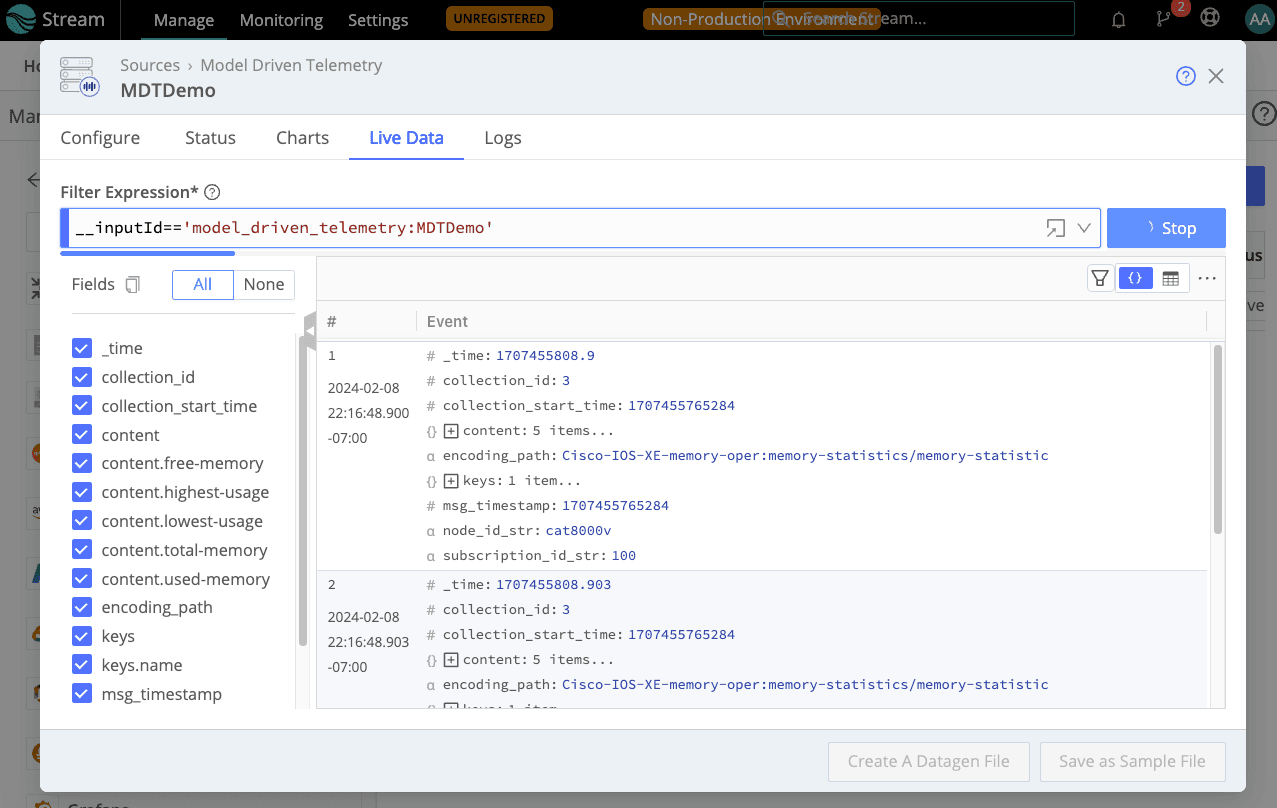
Expand the content array to see metric attributes within the message. You can break out these individual metrics to prepare them for downstream routing to observability platform destinations. To do this, create Cribl Pipelines and use Eval and Publish Metrics Functions to accomplish the desired transformations.
Wrapping Up
The benefits of Model Driven Telemetry shine when compared to its predecessor, SNMP:
SNMP is pull-based, not as granular, and impacts performance of the devices being monitored, especially as network monitoring demands increase.
MDT is subscription-based, highly granular, and performs well across large networks.
Cribl Stream, YANG, and NETCONF work together to give you visibility into and control of MDT data from your Cisco IOS XE network devices:
YANG Suite lets you explore data modules to understand what is available to monitor from your network devices.
You can use YANG Suite to build XML code bundles for MDT subscriptions and to push configurations to devices.
The Model Driven Telemetry Source, new in Cribl Stream 4.5, ingests MDT data for you to control, transform, and route to the destinations of your choice.