In this post we’ll walk through how to use the Auto Timestamp function to extract time fields from:
Events with multiple timestamps
Events with timestamp offset instead of full timestamps
Events with multiple timestamps
Assume we have events that look like this:
Sep 20 12:03:55 PA-VM 1,2019/09/20 13:03:58,CRIBL,TRAFFIC,end,2049,2019/09/20 14:03:58,314.817.108.226,10.0.0.102,314.817.108.226,10.0.2.65,cribl,,,incomplete,vsys1,untrusted,trusted,ethernet1/3,ethernet1/2,log-forwarding-default,2018/09/20 13:03:58,574326,1,53722,8088,53722,8088,0x400064,tcp,allow,296,296,0,4,2018/09/20 13:03:45,7,any,0,730277,0x0,United States,10.0.0.0-10.255.255.255,0,4,0,aged-out,0,0,0,0,,PA-VM,from-policy,,,0,,0,,N/A,0,0,0,0Notice how there are three timestamps, with two different formats and all showing different times:
Timestamp-1: Sep 20 12:03:55, Timestamp-2: 2019/09/20 13:03:58, Timestamp-3: 2019/09/20 14:03:58
When the Auto Timestamp function is used with default settings, it will inspect the first 150 bytes (configurable) of the event and extract the first valid timestamp that it encounters. In this case, it will be Timestamp-1.

But, what if we wanted to extract Timestamp-3? We have two options:
Change function’s Scan Offset to tell it to start looking for a valid timestamp deeper into the event. This will require precise knowledge of the location of the timestamp. E.g.,
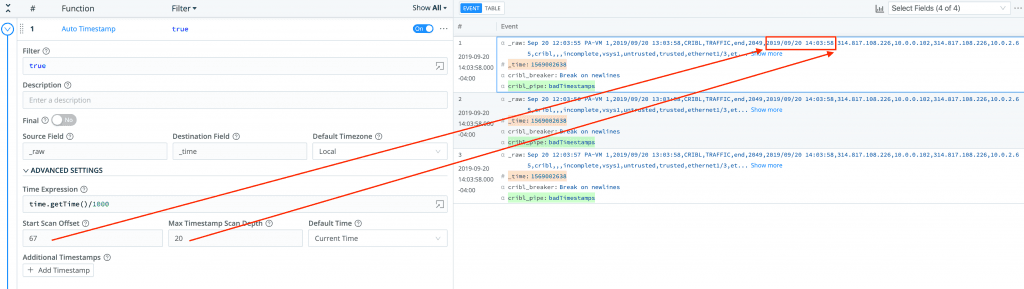
If the exact location is not known, then we can use Add Timestamp to define a regex to capture a timestamp pattern and provide corresponding timestamp format. E.g,

Events with timestamp offsets instead of full timestamps
Assume we have a dataset that look like this:
0.012 2020-02-05 17:35:53; Factorio 0.18.3 (build 49258, win64, alpha)
0.013 Operating system: Windows 10 (build 18363)
0.013 Program arguments: "E:\GOG\Factorio\bin\x64\factorio.exe" "--force-opengl"
0.013 Read data path: E:/GOG/Factorio/data
0.013 Write data path: C:/Users/Nate/AppData/Roaming/Factorio [626596/1907076MB]
0.013 Binaries path: E:/GOG/Factorio/bin
0.032 System info: [CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 2700X Eight-Core Processor, 16 cores, RAM: 6553/16310 MB, page: 9579/24406 MB, virtual: 4251/134217727 MB, extended virtual: 0 MB]
0.032 Display options: [FullScreen: 1] [VSync: 1] [UIScale: custom (150.0%)] [Native DPI: 1] [Screen: 255] [Special: lmw] [Lang: en]
0.036 Available displays: 1
0.036 [0]: \\.\DISPLAY1 - NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 {0x05, [0,0], 2560x1440, 32bit, 59Hz}
0.684 Initialised OpenGL:[0] GeForce GTX 1070/PCIe/SSE2; driver: 3.3.0 NVIDIA 432.00
0.684 [Extensions] s3tc:yes; KHR_debug:yes; ARB_clear_texture:yes, ARB_copy_image:yes
0.684 [Version] 3.3
0.684 Verbose GraphicsInterfaceOpenGL.cpp:896: [Caps] Tex:32768, TexArr:2048, TexBufSz:131072kB; TexUnits:192; UboSz:64kB
0.684 Graphics settings preset: very-high
0.684 Dedicated video memory size 8192 MB
1.095 Verbose PipelineStateObject.cpp:85: Time to load shaders: 0.411126 seconds.
1.149 Desktop composition is active.
1.150 Graphics options: [Graphics quality: high] [Video memory usage: all] [Light scale: 100%] [DXT: high-quality] [Color: 32bit]
1.150 [Max threads (load/render): 32/16] [Max texture size: 0] [Tex.Stream.: 0] [Rotation quality: normal] [Other: STDC] [B:0,C:0,S:100]Notice how only the first line has a full timestamp, all other lines have offsets off of that.
To properly assign accurate timestamp to events that follow Event 1 (Line 1) we have to use a cool property of Auto Timestamp (use Last Event’s Time) and then two other functions, namely Regex Extract and Eval.
Configure Auto Timestamp to use Last Event’s Time if it can’t extract a valid timestamp. This effectively means that all events will “inherit” Event 1’s time.
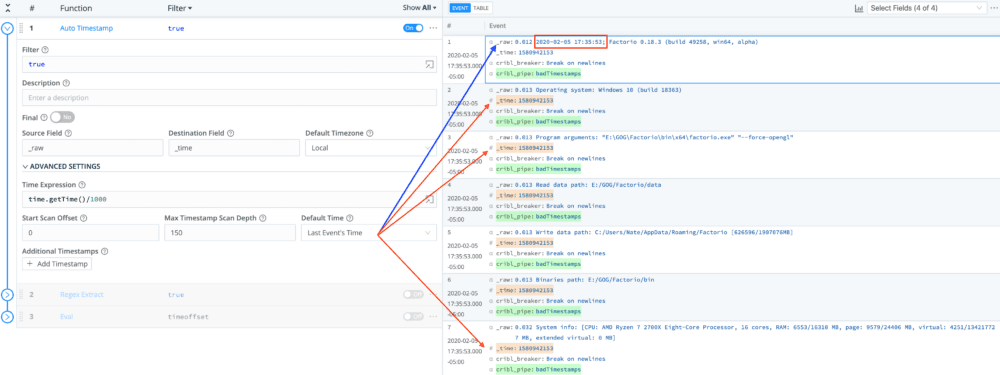
Use Regex Extract to extract the offset of all events, except for Event 1. Notice the negative lookahead in the Regex field.

Use Eval to add the offset to the
_timefield of each event. Convert it to number/float first.

The timeoffset field can be Removed in Eval or an internal field can be used instead. E.g. __timeoffset.
If you’re trying to deploy LogStream on your environment or have any questions please join our community Slack– we’d love to help you out. If you’re looking to join a fast-paced, innovative team drop us a line at hello@cribl.io– we’re hiring!







