In the realm of data management, understanding the details of how data is structured, stored, and accessed is crucial for IT professionals. Among the various approaches used today, schema-on-write stands out as a foundational model for dealing with data in a structured manner.
What is Schema-on-Write?
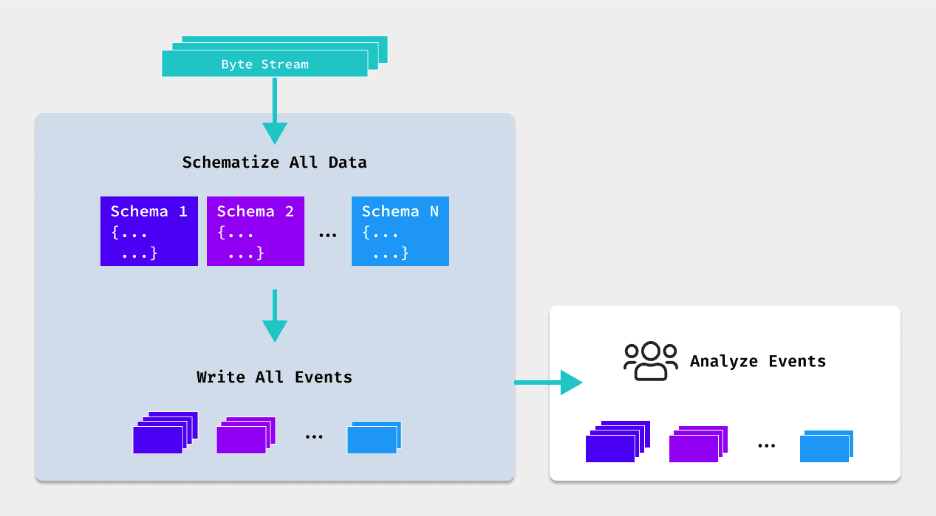
Schema-on-write is a data processing model where the schema (structure) of the data is defined and enforced before any data is ingested into a system of analysis. This approach requires a clear understanding of the data schema upfront. The process ensures that all data conforms to a predefined structure — and is particularly prevalent in traditional relational database systems and data warehousing solutions.
How does Schema-on-Write Work?
The schema-on-write process begins with the careful planning and design of the data schema, which includes defining data types, relationships, and constraints. Once the schema is established, data can be ingested into the system it needs to go into. However, this data must conform to the predefined schema, requiring any necessary transformations to be performed during the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process. This ensures that the data stored is immediately structured, optimized for query performance, and ready for analytical workloads.
Why is Schema-on-Write Important?
Schema-on-write systems are critical for scenarios where data integrity, consistency, and query performance are paramount. The model has the following benefits for organizations:
Data Integrity – is enhanced through Schema-on-Write, which mandates a structured format for data entry, ensuring consistency and precision. This elevates the reliability and quality of the data at hand.
Performance – implementing a predefined schema optimizes and indexes data, assisting with swift and efficient analysis. This enhances the speed and performance of data-centric applications.
Data Governance and Compliance – Schema-on-Write enables entities to uphold data governance standards, security protocols, and adhere to regulatory compliance by checking data against established criteria and constraints.
Data Integration – Schema-on-Write simplifies the process of data integration from different sources, including databases, APIs, and external systems. This allows organizations to forge a unified data perspective for informed analysis and strategic decision-making.
What are the most important Schema-on-Write Use Cases?
Schema-on-write systems are ideally suited for analytical applications where query performance and data integrity are crucial. Some of the most common use cases include:
Data warehousing – the model facilitates the structured ingestion, transformation, and consolidation of data into a centralized repository. It then serves as the backbone for comprehensive reporting and analytical insights.
Operational data stores – the model is invaluable by systematically organizing and converting operational data, either in real-time or on a near-real-time basis. It enables organizations with the data-driven insights needed for tactical operational decision-making.
Data migration and integration – Schema-on-Write is leveraged to transform and merge disparate data sources into a unified schema or format, streamlining the integration process.
Schema-on-Write Systems
Several database and data warehousing systems exemplify the schema-on-write approach, including:
Relational Databases: Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, and PostgreSQL are classic examples of relational databases employing a schema-on-write methodology.
Data Warehouses: Solutions like Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery provide scalable, cloud-based data warehousing that utilize schema-on-write for optimized analytics.
NoSQL Databases (Some Types): While NoSQL databases are often associated with schema-less or flexible schemas, certain types like MongoDB, Apache Cassandra, and Couchbase offer schema-on-write capabilities for specific use cases.