Threat detection and response (TDR) offers a comprehensive security approach. It uses tools and processes to monitor IT environments like networks, cloud platforms, endpoints, email gateways, and applications for security threats. Upon detection, TDR solutions can automatically take action to neutralize the threat and prevent any potential damage. By familiarizing yourself with the key concepts, components, and benefits of TDR, you’ll be better equipped to protect your organization’s existing environments and respond effectively to security incidents.
What is Threat detection and response (TDR)?
Threat detection and response (TDR) is a cybersecurity process that involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential security threats in real time. It integrates various technologies and methodologies to detect security incidents and respond appropriately to mitigate risks.
What is Threat Detection?
Threat Detection is the process of identifying potential security threats through monitoring, analyzing, and deciphering security data collected from various sources within an organization. This involves identifying patterns and anomalies that could indicate a cyber attack or security breach. Security incidents can come from internal or external actors and range from non-malicious incidents to targeted attacks.
What is Threat Response?
Threat Response is the collection of actions implemented to mitigate, contain, and remediate identified security threats. It includes strategies like isolating affected systems, applying patches, conducting forensic analysis, and restoring normal operations to reduce impact and prevent recurrence.
How does threat detection and response work?
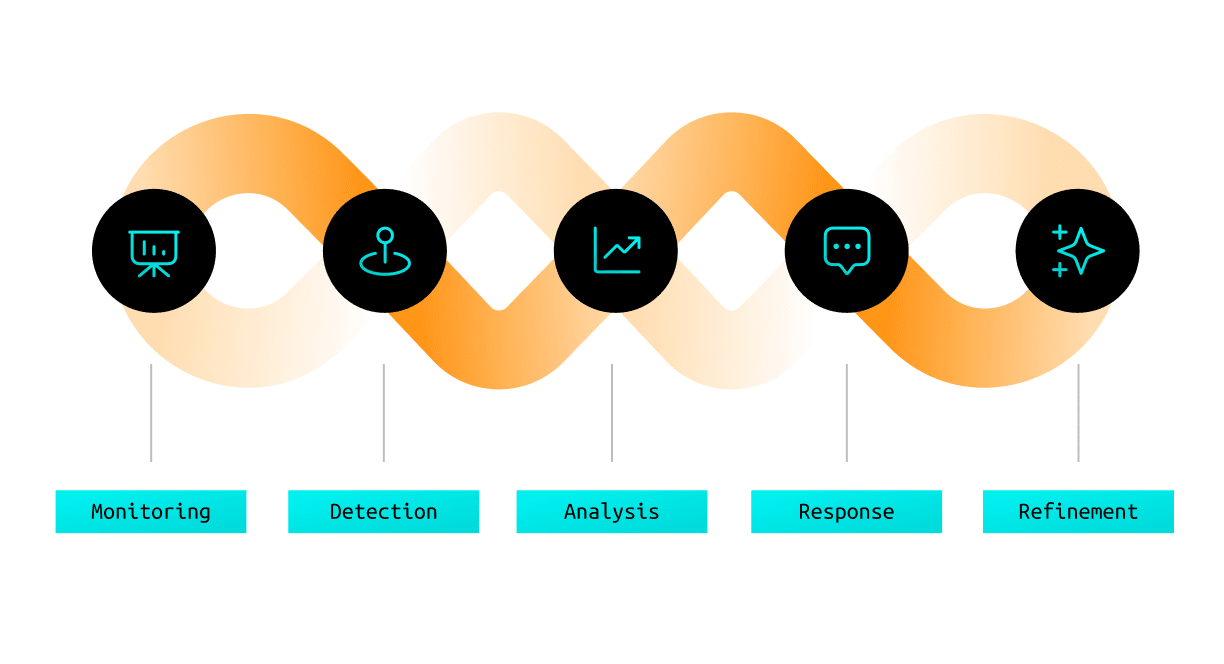
TDR works by continuously monitoring network traffic, system behaviors, and user activities to identify suspicious activities. Advanced technologies like machine learning and AI are used to analyze data and detect anomalies. When a threat is detected, automated and manual responses are triggered to contain and mitigate the impact, followed by a forensic analysis to understand the threat and improve future defenses.
The continuous cycle of monitoring, detection, analysis, and action includes:
Monitoring: Systems continuously collect and analyze data from various sources, including network traffic, endpoint activities, and user behaviors.
Detection: Advanced algorithms and rules identify potential threats based on known signatures, anomalies, or suspicious patterns.
Analysis: Security teams or automated systems investigate detected threats to determine their severity, scope, and potential impact.
Response: Based on the analysis, appropriate actions are taken to mitigate the threat, such as blocking malicious activities, isolating affected systems, or initiating incident response procedures.
Refinement: Lessons learned from each incident are used to improve detection capabilities and response strategies.
Key Components of Threat detection and response
Threat detection and response systems typically comprise several interconnected components that work together to provide comprehensive security coverage. Here are the key components:
Security information and event management (SIEM)
SIEM systems collect and analyze log and event data from various sources to detect security incidents. They provide real-time monitoring and historical analysis to discover threats and support compliance efforts.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
EDR solutions continuously monitor endpoints to detect and respond to advanced threats. They offer visibility into endpoint activities and enable rapid investigation and containment of malicious activities.
Extended detection and response (XDR)
XDR is an integrated approach that centralizes and correlates data from across security layers. It enhances detection accuracy and streamlines the response process through unified visibility and automated analysis.
Identity threat detection and response (ITDR)
ITDR focuses on monitoring and protecting user identities. It detects suspicious behaviors that indicate compromised user accounts and responds to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Threat intelligence
Threat intelligence provides up-to-date information about current and emerging threats, helping organizations stay ahead of potential attacks. Many security-related tools and sites provide different levels of information and specific needs will be used case-based.
Vulnerability management
Vulnerability management is the practice of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating security vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Regular scanning and patching help minimize the attack surface and mitigate exploitable weaknesses.
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR)
SOAR platforms integrate various security tools and automate response processes. They enable efficient incident management by automating repetitive tasks and orchestrating complex workflows across multiple security components.
Managed detection and response (MDR)
MDR services provide outsourced security monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities, often supplementing an organization’s internal security team.
Benefits of threat detection and response
Early detection of sophisticated and evasive threats
Identify advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other complex attacks that may evade traditional security measures.
Improved protection and reduced damage
Proactive threat management limits the impact of cyber attacks, protecting sensitive data and critical system operations from potential harm.
Enhanced visibility across your environment
Enhanced visibility and centralized monitoring enable quicker identification of security incidents, enabling better decision-making and resource allocation.
Proactive Approach
Stay ahead of attackers by actively searching for indicators of compromise and potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This forward-thinking approach allows security teams to identify and neutralize threats in their earliest stages, often preventing incidents entirely rather than simply responding after damage has occurred.
Real-World Examples of Threat Detection and Response in Action
Effective TDR often comes down to speed. One large customer detected an indicator of compromise (IOC) and needed to investigate fast. Their existing system required pulling 26 TB of archived data, with a 24-hour retrieval window per the vendor’s SLA. But that wasn’t fast enough. They turned to Cribl. Using federated search, the team was able to query across regions, isolate just the three days of relevant data, and retrieve 1.2 million targeted events in under 90 minutes. Instead of waiting a full day, they resumed their investigation the same night and were able to take action before the threat escalated.
Challenges in Threat Detection & Response—and How Cribl Solves Them
Effectively identifying, investigating, and responding to threats is a critical function of security operations. However, organizations still face persistent challenges in TDR. The immense scale of data, complex environments, and limited resources can hinder teams and increase organizational risk.
Data Overload and Alert Fatigue
Security teams are overwhelmed by the daily flood of security data and false positives, leading to critical alerts being missed or delayed. Siloed data sources and high event volumes make it difficult to prioritize genuine threats.
How Cribl Solves It: Cribl Stream enables organizations to filter, route, and enrich telemetry before it reaches SIEMs or other analytics tools. This targeted approach dramatically reduces noise and data volume, helping teams focus on high-fidelity alerts and actionable insights while optimizing storage and processing costs.
Lack of Data Normalization and Enrichment
Inconsistent log formats and incomplete event data slow down investigations and automated detection. Security tools struggle to correlate events across diverse streams, reducing the effectiveness of threat hunting.
How Cribl Solves It: With Cribl Stream’s powerful data transformation features, teams can normalize and enrich telemetry in flight, adding context, converting formats, and bringing together data from multiple sources. This results in analytics-ready, unified datasets that accelerate investigations and drive more accurate detection across the environment.
High Costs and Inflexibility of Security Analytics Tools
Traditional SIEMs and analytics platforms often force organizations to ingest or keep all data in a proprietary format, leading to ballooning licensing and infrastructure expenses and locking teams into rigid vendor ecosystems.
How Cribl Solves It: Using Cribl’s vendor-agnostic architecture, organizations can route different data types to optimize storage and select the appropriate analytics platforms, while retaining full control over their data. This flexibility cuts costs, avoids vendor lock-in, and ensures long-term access to valuable security insight.
Delays in Incident Response Due to Slow Access to Historical Data
Investigating advanced threats frequently requires access to months or even years of historical telemetry. However, retrieving cold storage data for analysis is often slow or cost-prohibitive with legacy tools.
How Cribl Solves It: Cribl Search empowers teams to query data directly at the source, whether it’s stored locally, in object stores, or across the cloud—without having to rehydrate or duplicate it. This instant, federated search accelerates incident investigations and threat hunting, transforming historical data into a live resource for security teams.
Gaps in Visibility from Distributed and Dynamic Environments
Hybrid and cloud-native infrastructures generate telemetry from countless sources in varying formats and locations, making it hard for security teams to gain a unified view of all activity or maintain compliance.
How Cribl Solves It: With Cribl Edge and Stream, organizations can collect, standardize, and centrally manage telemetry from cloud, on-premises, and edge sources. This end-to-end visibility strengthens monitoring, ensures compliant data handling, and supports a proactive security posture across evolving environments.
Threat Detection & Response FAQs
What is Threat Detection & Response?
TDR stands for Threat Detection and Response. It’s a cybersecurity approach that continuously monitors your systems for suspicious activity. In real-time, TDR can identify, analyze, and respond to security threats, minimizing potential damage and mitigating risks.
What are the stages or processes of the threat detection and response process?
The threat detection and response process typically includes several stages, often defined as a cycle to ensure continuous improvement and robust security posture.
Preparation. Develop policies, procedures, and tools. Train staff on cyber threat detection & incident response. Set a baseline for anomaly detection.
Detection. Utilize diverse methods like signature-based, anomaly-based, heuristic, and behavioral analysis for threat detection. Continuously monitor network traffic, logs, and user activity with tools such as IDS, SIEM, and security solutions.
Analysis. Prioritize threats based on severity and impact. Conduct detailed analysis to confirm and understand threats.
Containment. Implement short-term measures to contain the threat and follow up with long-term strategies for full control.
Eradication. Identify and eliminate the root cause of the threat. Remove malicious files, patch vulnerabilities, and update systems as needed.
Recovery. Restore systems to normal, monitor for threats, and validate remediation effectiveness.
Post-Incident Activities. Conduct post-mortem analysis to review the incident response process, document actions taken, and update policies/tools for improvement.
What’s the difference between threat detection and incident response?
The primary difference lies in their respective purposes and processes. Threat detection identifies potential security threats or vulnerabilities in a system or network by monitoring network traffic, logs, and user behavior to detect anomalies or signs of malicious activity. While on the other hand incident response addresses and manages the aftermath of a detected security breach or cyber attack to limit damage, reduce recovery time, and minimize costs. This includes containing the threat, eradicating the cause, recovering from the effects, and implementing measures to prevent future incidents.