SIEM is a cybersecurity technology that plays a critical role in detecting, investigating, and responding to security threats. It provides a centralized platform for monitoring and analyzing security data, offering real-time insights into potential threats and suspicious activity. By correlating events across various systems, SIEM enhances your ability to identify and respond to cyber threats proactively, improving operational efficiency and helping to maintain a robust security posture.
What is SIEM?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a powerful cybersecurity solution that provides a real-time, comprehensive view of an organization’s security landscape. By collecting, analyzing, and correlating data from various sources—whether on-premises or in the cloud—SIEM delivers actionable insights for IT and security leaders to safeguard their networks against cyber threats.
Originally designed as a passive compliance tool for collecting log data, it has evolved into a proactive defense system. Today, it not only monitors security events but also offers real-time analysis and advanced threat detection, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to cyberattacks. This shift reflects a broader change in cybersecurity, moving from passive oversight to active threat prevention.
SIEM combines two critical functions:
Security Information Management (SIM): This component collects, stores, and manages log data generated by various hardware and software applications.
Security Event Management (SEM): SEM handles real-time monitoring, correlation of security events, and alert notifications to provide immediate visibility into potential threats.
By integrating SIM and SEM, SIEM systems empower IT professionals to better manage security across complex environments, ensuring a robust, scalable defense against evolving cyber threats. As the threat landscape grows more sophisticated, the role of SIEM has become more important. Whether monitoring cloud-based or on-premises networks, SIEM solutions help security and IT teams maintain compliance, detect anomalies, and respond to security incidents in real-time, ensuring continuous protection.
The two functions work in tandem to provide a holistic view of an organization’s information security landscape.
How SIEM Works: Key Stages in Threat Detection and Response
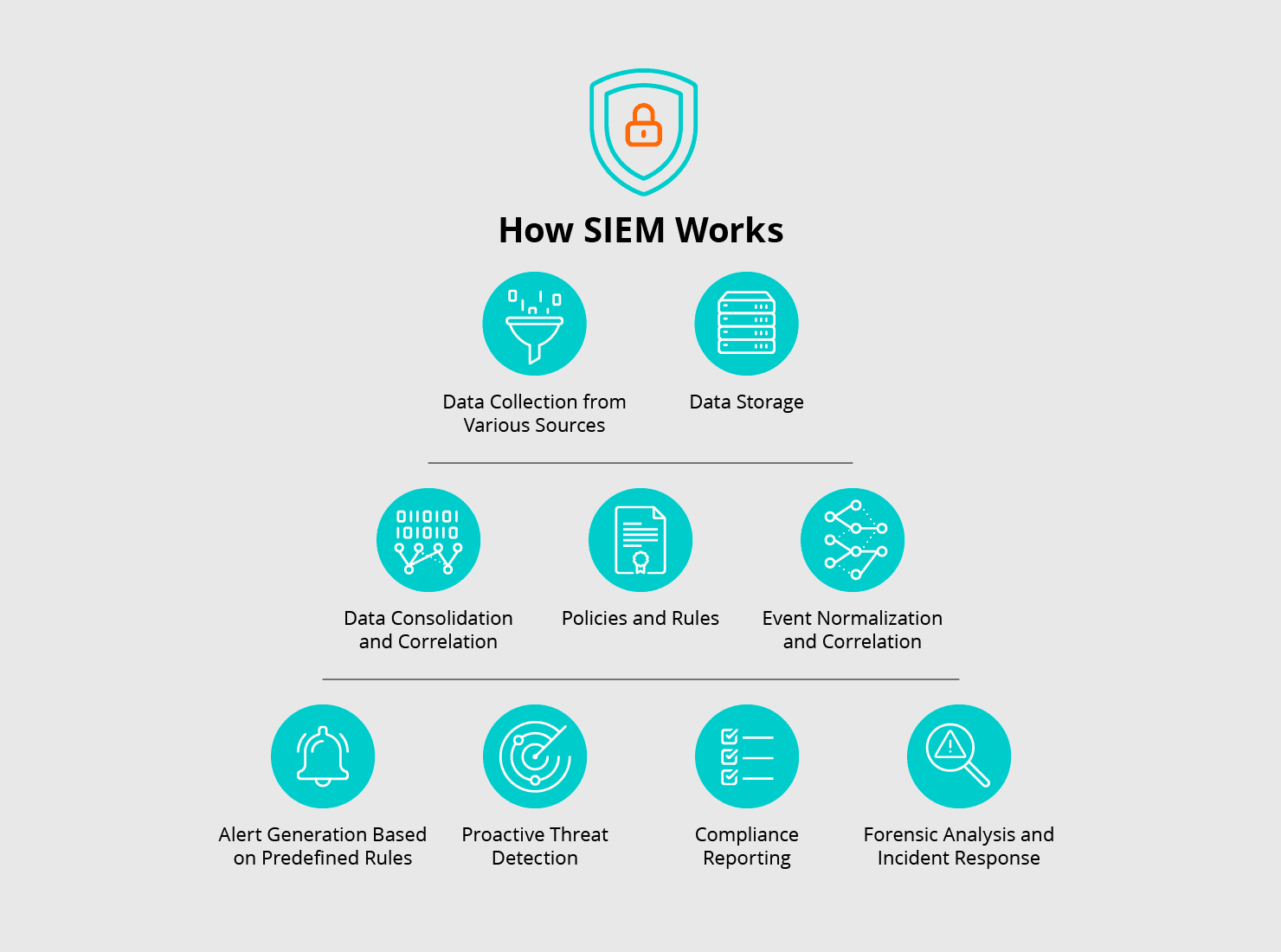
SIEM operates through a series of essential stages, including data collection, storage, event normalization, and correlation. By generating alerts based on predefined rules and using advanced algorithms for proactive threat detection, it adapts to the evolving security needs of remote, hybrid, and in-office teams.
Data Collection from Multiple SourcesSIEM begins with data collection, the foundation of any security analysis. It gathers data from a wide range of sources, such as firewalls, servers, routers, and endpoint devices, ensuring comprehensive visibility across your network.
Data StorageOnce collected, the data is stored in a secure SIEM repository. This storage system archives raw data for both real-time monitoring and historical analysis. It enables organizations to investigate past events while keeping track of ongoing activities.
Data Consolidation and CorrelationData in isolation can be overwhelming and unstructured. SIEM systems use advanced algorithms to consolidate and correlate logs from different sources, transforming scattered data points into meaningful insights. This process allows for the detection of suspicious patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Policies and RulesSIEM operates under predefined policies and rules that define what constitutes normal versus suspicious activity. These rules consider key factors like IP addresses, device management status, and other behavioral indicators, allowing IT teams to quickly identify potential security threats.
Event NormalizationNormalization involves standardizing log entries and events into a common format. This step simplifies correlation by enabling the comparison of data from various sources, making it easier to detect patterns, anomalies, and potential threats.
Alert GenerationOnce data is normalized and analyzed according to the predefined rules, SIEM generates alerts for any activity that deviates from normal behavior. These alerts act as the first line of defense, prompting IT and security teams to take immediate action.
Proactive Threat DetectionModern SIEM systems go beyond reactive security measures. By incorporating machine learning and behavioral analytics, they proactively identify potential threats before they escalate into full-blown security breaches. This forward-looking approach helps organizations stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
Compliance ReportingMeeting regulatory requirements is an ongoing challenge for businesses. SIEM simplifies compliance by generating detailed reports that help organizations adhere to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others. Features like data masking are critical in ensuring sensitive information is protected while maintaining compliance.
Forensic Analysis and Incident ResponseIn the event of a security breach, SIEM provides essential tools for forensic analysis. By retracing the steps leading up to the incident, security teams can gain valuable insights into how the breach occurred and how to prevent similar incidents in the future. SIEM also supports incident response by delivering the necessary data to contain and mitigate the threat.
Types of SIEM
SIEM is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it comes in various forms, each with its own set of features, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the SIEM solution that best fits your organization’s needs. Let’s explore the main types of SIEM and what sets them apart.
On-Premises / In-House SIEM
On-premises SIEM solutions are installed and operated from a client’s in-house server. This type of SIEM gives you complete control over your data and the SIEM software itself, much like having a home library where you know each book’s exact location.
Pros:
Complete control over data and configurations
Easier to meet specific compliance requirements
No reliance on external networks for data transfer if all servers are in-house
Cons:
High upfront costs for hardware and software
Requires in-house expertise for maintenance and updates
Scalability can be challenging and costly
If employees are remote, external networks will still be involved for endpoints
Cloud SIEM
Cloud SIEM solutions are hosted on the provider’s cloud infrastructure. They offer the benefits of SIEM without the need for in-house hardware, akin to using a public library where maintenance is taken care of for you.
Pros:
Lower upfront costs
Easy scalability
Automatic updates and maintenance
Cons:
Potential data privacy concerns if not properly secured
Reliance on the provider’s network and uptime
May not meet specific compliance requirements depending on the region
Managed SIEM
Managed SIEM solutions are a hybrid approach, combining the features of both on-premises and cloud SIEM while adding the benefit of being managed by third-party experts. Think of it as a curated library service where experts recommend books based on your reading habits.
Pros:
Expert management and monitoring
Customizable to specific needs
Focus on core business activities
Cons:
Potential for less control over data
Dependence on the service provider’s expertise
SIEM Capabilities
SIEM capabilities range from log management and event correlation to incident monitoring and response. These core features enable SIEM to offer a range of benefits, including but not limited to advanced visibility, enhanced security, and streamlined IT operations.
Log Management
Log management is the cornerstone of any SIEM solution. It involves the collection, storage, and analysis of log data from various sources within an organization. This is akin to gathering raw materials before crafting a product; without logs, SIEM would lack the fundamental data needed for analysis and action. As the use of a SIEM grows, log volume does become a concern as many teams continue to look to reduce log volume to lower infrastructure costs.
Event Correlation
Event correlation is the process of linking related records and identifying patterns among them. This feature allows SIEM to transform isolated data points into meaningful insights.
Incident Monitoring and Response
Incident monitoring and response are where SIEM truly shines. It’s not just about identifying issues but also about providing actionable insights for resolving them. This capability serves as the control center during a security incident, guiding the response team through the chaos to a resolution.
Threat Identification
Threat identification goes beyond mere data collection and dives into proactive security. Using advanced algorithms and machine learning, SIEM can identify potential threats before they become active attacks.
Compliance Reporting
Compliance reporting is often considered a byproduct of SIEM, but it’s a crucial feature. SIEM solutions generate detailed reports that help organizations meet various regulatory requirements. This is not just about ticking boxes; it’s about maintaining a standard of security that’s recognized and mandated by governing bodies.
SIEM Best Practices
SIEM best practices include defining clear goals for your implementation, centralizing your data, and optimizing the data ingestion process. Regular updates to SIEM rules and signatures, proper data retention, and staff training are also crucial for maximizing SIEM effectiveness. It should be on every IT professional’s project list to undertake a SIEM optimization regularly.
Define Clear Goals for Your SIEM Implementation
Before diving into technical details, it’s crucial to establish the objectives of your SIEM implementation, whether they involve compliance, real-time monitoring, or incident response. Clear goals guide implementation strategies and performance evaluation.
Centralize Your Data
Data centralization is the foundation upon which SIEM operates. It involves aggregating data from various sources into a single repository, enhancing the system’s ability to correlate events and generate meaningful insights. Think of it as creating a centralized command center for security data.
Optimize Data Ingestion Process
Ensuring high-quality and timely data ingestion is critical. Optimization of this process ensures that the SIEM system receives accurate and up-to-date information, enhancing its analytical capabilities and overall effectiveness.
Regularly Update SIEM Rules and Signatures
The cybersecurity landscape is ever-changing, and your SIEM solution needs to adapt accordingly. Regularly updating rules and signatures ensures that your system can identify the latest threats and vulnerabilities, keeping your security posture robust.
Ensure Proper Data Retention
Data retention is not just a compliance requirement but also a practical necessity. Properly retaining data allows for historical analysis, which can be invaluable for identifying long-term trends and improving your security measures.
Train Staff on SIEM Operations and Threat Response
A SIEM system is only as effective as the people operating it. Training your staff on SIEM operations and threat response equips them with the skills needed to maximize the system’s capabilities and respond effectively to security incidents.
Conduct Regular Reviews/Audits
Regular reviews and audits serve as a health check for your SIEM system. They help identify any gaps or inefficiencies, providing an opportunity for continuous improvement.
Integrate SIEM with Other Security Tools
SIEM is not a standalone solution; it’s part of a larger security ecosystem. Integrating it with other security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems enhances its capabilities and provides a more holistic view of your security landscape.
Automate Workflows
Automation is the key to efficiency. Automating workflows within your SIEM system not only speeds up processes but also reduces the likelihood of human error, making your security operations more reliable and effective.
How Can Cribl help you with SIEM?
Cribl Stream is a powerful observability pipeline that integrates seamlessly with various SIEM systems, helping organizations maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of their security information and event management. By optimizing the way data is ingested, processed, and routed, Cribl Stream enables SIEM platforms to perform at their best, reducing noise, cutting costs, and improving overall security outcomes.
Here’s how Cribl Stream can help with SIEM:
Data Optimization and FilteringSIEM systems often struggle with handling vast volumes of log data, which can lead to inefficiencies and unnecessary costs. Cribl Stream allows you to filter out irrelevant or redundant data before it reaches your SIEM. This reduces data ingestion costs and improves the system’s focus on high-value information. It ensures that your SIEM processes only the most actionable data, enhancing performance and reducing noise from false positives.
Flexible Data RoutingCribl Stream gives you the flexibility to route data to multiple destinations, including cloud storage, SIEMs, or other analytics tools. This allows you to send relevant data while archiving or routing less critical data to cheaper storage options. By doing this, Cribl Stream helps you manage storage costs without sacrificing visibility or security insights.
Normalization and EnrichmentFor SIEMs to operate efficiently, data must be normalized and enriched. Cribl Stream normalizes data into consistent formats, making it easier for SIEMs to correlate events across various sources. Additionally, Cribl can enrich log data with additional context (e.g., geolocation or threat intelligence) before forwarding it to the SIEM, enhancing the quality of the analysis and helping teams respond more effectively to potential threats.
Real-Time Monitoring and ProcessingCribl Stream provides real-time log and event processing capabilities, ensuring that your SIEM receives up-to-date, actionable data. This is crucial for real-time threat detection and response, allowing security teams to quickly identify and react to security incidents as they occur.
Cost ManagementSIEM costs can quickly escalate with increasing data volumes. Cribl Stream helps organizations reduce their SIEM-related expenses by controlling data volumes, filtering out low-value logs, and providing compression options before data is ingested. This not only reduces licensing costs but also ensures that your SIEM is more focused and efficient in detecting actual threats.
Improved SIEM ScalabilityAs your organization grows, so does the volume of data that needs to be processed by your SIEM. Cribl Stream scales effortlessly to handle growing data volumes while ensuring that only relevant and enriched data reaches your SIEM platform. This helps maintain the performance of your SIEM solution even as data environments expand.
Seamless IntegrationCribl Stream integrates with all major SIEM platforms, including Splunk, IBM QRadar, and ArcSight, providing a seamless way to enhance existing SIEM deployments. Whether you’re using on-premises or cloud-based SIEM systems, Cribl Stream ensures that your data pipelines are optimized for performance, cost-efficiency, and reliability.
In summary, Cribl Stream enhances your SIEM by optimizing data ingestion, reducing costs, and delivering high-quality, enriched data for improved threat detection and response. It helps your SIEM operate more efficiently, ensuring better security outcomes and more effective use of resources.
What is a SIEM?
SIEM, or Security Information and Event Management, is a cybersecurity tool that aggregates and analyzes security-related data from various sources in real-time. Its primary function is to provide comprehensive visibility into an organization’s IT infrastructure, enabling the detection and response to potential security threats.
What is the difference between SIM and SEM?
Security Information Management (SIM) focuses on the collection, storage, and analysis of log data for compliance and reporting purposes. Security Event Management (SEM), on the other hand, is concerned with real-time monitoring, correlation, and alerting of security events. Together, they form the backbone of SIEM, combining long-term data analysis with immediate threat detection and response.
What are the 3 types of SIEM?
The three types of SIEM solutions include On-Premise SIEM, Cloud-Based SIEM and Hybrid SIEM.
What is Cribl Stream, and how does it work with SIEM?
Cribl Stream is an observability pipeline that allows organizations to collect, process, and route data from various sources. It helps optimize the data flow into SIEM systems by filtering, normalizing, enriching, and routing data, ensuring that SIEMs receive only the most relevant and actionable data. This improves the efficiency and effectiveness of SIEM operations.
How does Cribl Stream help reduce SIEM costs?
Cribl Stream reduces SIEM costs by filtering out unnecessary or redundant data before it reaches the SIEM, thus lowering the amount of data that needs to be processed and stored. It can also compress and route less critical data to cheaper storage solutions, minimizing expensive data ingestion and licensing costs.
Can Cribl Stream work with any SIEM platform?
Yes, Cribl Stream integrates seamlessly with all major SIEM platforms, including Splunk, CrowdStrike, IBM QRadar, Exabeam, and others. Whether your SIEM is on-premises or cloud-based, Cribl can be used to optimize data flow and processing.
What benefits does Cribl Stream offer in terms of data enrichment?
Cribl Stream can enrich raw data with additional context, such as geolocation, threat intelligence, or custom metadata, before it reaches the SIEM. This enrichment provides greater insights into security events, allowing SIEM systems to perform more detailed analysis and helping security teams respond more effectively to potential threats.
How does Cribl Stream improve SIEM scalability?
Cribl Stream helps SIEM systems scale by filtering and optimizing data streams, ensuring that only high-value data reaches the SIEM. This allows your SIEM to handle larger volumes of data efficiently as your organization grows, without becoming overwhelmed by irrelevant or redundant information.
Does Cribl Stream support real-time data processing for SIEM?
Yes, Cribl Stream processes data in real time, ensuring that your SIEM system receives up-to-date information. This is critical for real-time threat detection and response, as it enables security teams to identify and address security incidents as they happen.
How does Cribl Stream enhance compliance reporting in SIEM?
By optimizing and enriching data streams, Cribl Stream ensures that SIEMs receive accurate, relevant information needed for compliance reporting. It helps generate detailed reports that meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others, while also enabling data masking to protect sensitive information.
What kind of data can Cribl Stream handle for SIEM?
Cribl Stream can ingest and process data from a wide variety of sources, including firewalls, servers, routers, cloud services, endpoint devices, and more. It supports structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making it a versatile tool for optimizing SIEM data flow.